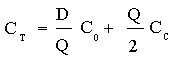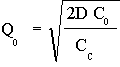Spreadsheet Models for Managers
Getting Access to Spreadsheet Models for Managers
If  you use Excel to model businesses, business processes, or
business transactions, this course will change your life. You’ll learn how to create tools for yourself that will amaze
even you. Unrestricted use of this material is available in two ways.
you use Excel to model businesses, business processes, or
business transactions, this course will change your life. You’ll learn how to create tools for yourself that will amaze
even you. Unrestricted use of this material is available in two ways.
- As a stand-alone Web site
- It resides on your computer, and you can use it anywhere. No need for Internet access.
- At this Web site
- If you have access to the Internet whenever you want to view this material, you can purchase on-line access. Unlimited usage. I’m constantly making improvements and you’ll get them as soon as they’re available.
To Order On Line
| Order "Spreadsheet Models for Managers, on-line edition, one month" by credit card, for USD 69.95 each, using our secure server, and receive download instructions by return email. |
| Order "Spreadsheet Models for Managers, on-line edition, three months" by credit card, for USD 199.00 each, using our secure server, and receive download instructions by return email. |
| Order "Spreadsheet Models for Managers, downloadable hyperbook edition" by credit card, for USD 199.00 each, using our secure server, and receive download instructions by return email. |
To Order by Mail
Make your check payable to Chaco Canyon Consulting, for the amount indicated:
|
And send it to: Chaco Canyon Consulting 700 Huron Avenue, Suite 19C Cambridge, MA 02138 |
To use the course software you’ll need some other applications, which you very probably already have. By placing your order, you’re confirming that you have the software you need, as described on this site.

Spreadsheet Models for Managers
This reading is especially relevant for Session 11Economic Order Quantity
To understand why the Economic Order Quantity is given by the formula in the session notes, we must understand why the minimum value of Ct, total cost, occurs when the two contributing terms are equal. Remember that the total cost per unit has two components — the cost of ordering and the cost of carrying inventory.
|
|
(1) |
This total cost per unit, of course, isn’t really the total cost, despite our use of the word “total.” This total cost ignores the cost of the unit itself. But since we’re assuming that this element of cost is independent of Q, the task of finding the optimal value of Q reduces to the task of minimizing the sum of the two terms above.
- where
- D is annual demand (units)
Q is quantity per order
C0 is cost per order
Cc is carrying Cost of inventory (dollars per unit per year)
To learn why this strange coincidence occurs, you usually need to use Calculus, but we can give a pretty good argument without it. Let’s work a simpler problem first. We will find the value of Q that minimizes the expression
<snip>…
 Some of the page you’ve been reading has been suppressed from this sampler. To see the complete version of this article, why not order the full course? It’s available at this Web site or in downloadable format.
Some of the page you’ve been reading has been suppressed from this sampler. To see the complete version of this article, why not order the full course? It’s available at this Web site or in downloadable format.
| Order "Spreadsheet Models for Managers, on-line edition, three months" by credit card, for USD 199.00 each, using our secure server, and receive download instructions by return email. |
| Order "Spreadsheet Models for Managers, downloadable hyperbook edition" by credit card, for USD 199.00 each, using our secure server, and receive download instructions by return email. |
…<end snip>
So
|
|
(10) |
Last Modified: Sunday, 03-Aug-2025 03:54:37 EDT
Although the assumption of constant demand is critical to justifying the derivation of the formula for Economic Order Quantity, most problems don’t satisfy that requirement in the strict sense. But EOQ is nevertheless a valuable concept in two kinds of circumstances. The first case is when the time scale of the inventory management decisions is much shorter than the time scale of the variations in demand. And the second is when the fluctuations in demand occur much more rapidly than the inventory management decisions.
These two approximations occur repeatedly in modeling problems. Watch for opportunities to apply them elsewhere.