When we disagree, the sources of our disagreement can often be differing assumptions that are outside our mutual awareness. Working out these differences is a lot easier when we know what they are, but sometimes surfacing the assumptions can be risky. Here's part two of a method based on the Johari window. See "Assumptions and the Johari Window: I," Point Lookout for September 27, 2006, for Part I, where we discussed Open and Blind assumptions. The last two quadrants of the Johari Window are Hidden and Unknown.
- My hidden assumptions
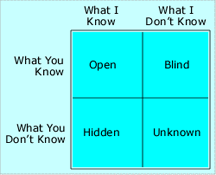 Hidden assumptions are those that I know I'm making, but you don't. For instance, I might believe that you'll benefit from a particular organizational decision, and that's why you're advocating for that decision. Even though I might be mistaken, I might still make the assumption — and conceal it.
Hidden assumptions are those that I know I'm making, but you don't. For instance, I might believe that you'll benefit from a particular organizational decision, and that's why you're advocating for that decision. Even though I might be mistaken, I might still make the assumption — and conceal it.- Sometimes exposing a hidden assumption is easy, and exposure can lead to relief in the group, as when the assumer doesn't realize that nobody else knows about the assumption.
- And sometimes exposing hidden assumptions is difficult, because the assumer might actively hide them. When asked, the assumer might actually deny hiding anything. Even upon admitting making the assumption, assumers can feel "caught," and might experience guilt or shame. Defensiveness can follow.
- One approach to resolution is to first ensure safety, and then search for hidden assumptions by simply asking for disclosure. Often this exposes the accidentally hidden assumptions with relatively low risk.
- Use the same method for intentionally hidden assumptions, but wait until the second or third pass, after people are more comfortable with the process, and after you've built some success with the easier types of out-of-awareness assumptions.
- My unknown assumptions
- Unknown assumptions Tackle the more challenging kinds
of assumptions after you've
built some success
with the easier onesare those that I don't know I'm making, and you don't know about them either. Such assumptions are like land mines whose locations are long forgotten. They're the most difficult to surface, because we're both unaware they exist. And when we do find one, the discovery can trigger strong feelings for us both. - Joint exploration for unknown assumptions can be risky, because either or both of the explorers can be caught making assumptions they don't know about. The surprise itself can be unsettling. To ease the surprise, save this pane of the Johari window for last, when experience with uncovering assumptions in the other panes can be a resource for both parties. And be sure that everyone is rested — take breaks, or split the session if necessary.
In any impasse, it's likely that there are assumptions of all four kinds — Open, Blind, Hidden, and Unknown. When the assumption that there are assumptions of all four kinds is itself Blind, Hidden, or Unknown, the chances of resolving the others are small. Talking about the possibility of Open, Blind, or Unknown assumptions eases the task of resolving them together. ![]() First issue in this series
First issue in this series ![]() Top
Top ![]() Next Issue
Next Issue
Are you fed up with tense, explosive meetings? Are you or a colleague the target of a bully? Destructive conflict can ruin organizations. But if we believe that all conflict is destructive, and that we can somehow eliminate conflict, or that conflict is an enemy of productivity, then we're in conflict with Conflict itself. Read 101 Tips for Managing Conflict to learn how to make peace with conflict and make it an organizational asset. Order Now!
Your comments are welcome
Would you like to see your comments posted here? rbrenaXXxGCwVgbgLZDuRner@ChacDjdMAATPdDNJnrSwoCanyon.comSend me your comments by email, or by Web form.About Point Lookout
 Thank you for reading this article. I hope you enjoyed it and
found it useful, and that you'll consider recommending it to a friend.
Thank you for reading this article. I hope you enjoyed it and
found it useful, and that you'll consider recommending it to a friend.
This article in its entirety was written by a human being. No machine intelligence was involved in any way.
Point Lookout is a free weekly email newsletter. Browse the archive of past issues. Subscribe for free.
Support Point Lookout by joining the Friends of Point Lookout, as an individual or as an organization.
Do you face a complex interpersonal situation? Send it in, anonymously if you like, and I'll give you my two cents.
Related articles
More articles on Personal, Team, and Organizational Effectiveness:
 Mastering Meeting Madness
Mastering Meeting Madness- If you lead an organization, and people are mired in meeting madness, you can end it. Here are a few
tips that can free everyone to finally get some work done.
 Discussion Distractions: II
Discussion Distractions: II- Meetings are less productive than they might be, if we could learn to recognize and prevent the most
common distractions. Here is Part II of a small catalog of distractions frequently seen in meetings.
 The Reification Error and Performance Management
The Reification Error and Performance Management- Just as real concrete objects have attributes, so do abstract concepts, or constructs. But attempting
to measure the attributes of constructs as if they were the attributes of real objects is an example
of the reification error. In performance management, committing this error leads to unexpected and unwanted
results.
 Paradoxical Policies: I
Paradoxical Policies: I- Although most organizational policies are constructive, many are outdated or nonsensical, and some are
actually counterproductive. Here's a collection of policies that would be funny if they weren't real.
 Disjoint Awareness
Disjoint Awareness- In collaborations, awareness of how our own work might interfere with the work of others is essential.
Unless our awareness of others' work — and their awareness of ours — matches reality, the
collaboration's objective is at risk.
See also Personal, Team, and Organizational Effectiveness for more related articles.
Forthcoming issues of Point Lookout
 Coming October 1: On the Risks of Obscuring Ignorance
Coming October 1: On the Risks of Obscuring Ignorance- When people hide their ignorance of concepts fundamental to understanding the issues at hand, they expose their teams and organizations to a risk of making wrong decisions. The organizational costs of the consequences of those decisions can be unlimited. Available here and by RSS on October 1.
 And on October 8: Responding to Workplace Bullying
And on October 8: Responding to Workplace Bullying- Effective responses to bullying sometimes include "pushback tactics" that can deter perpetrators from further bullying. Because perpetrators use some of these same tactics, some people have difficulty employing them. But the need is real. Pushing back works. Available here and by RSS on October 8.
Coaching services
I offer email and telephone coaching at both corporate and individual rates. Contact Rick for details at rbrenaXXxGCwVgbgLZDuRner@ChacDjdMAATPdDNJnrSwoCanyon.com or (650) 787-6475, or toll-free in the continental US at (866) 378-5470.
Get the ebook!
Past issues of Point Lookout are available in six ebooks:
- Get 2001-2 in Geese Don't Land on Twigs (PDF, )
- Get 2003-4 in Why Dogs Wag (PDF, )
- Get 2005-6 in Loopy Things We Do (PDF, )
- Get 2007-8 in Things We Believe That Maybe Aren't So True (PDF, )
- Get 2009-10 in The Questions Not Asked (PDF, )
- Get all of the first twelve years (2001-2012) in The Collected Issues of Point Lookout (PDF, )
Are you a writer, editor or publisher on deadline? Are you looking for an article that will get people talking and get compliments flying your way? You can have 500-1000 words in your inbox in one hour. License any article from this Web site. More info
Follow Rick
Recommend this issue to a friend
Send an email message to a friend
rbrenaXXxGCwVgbgLZDuRner@ChacDjdMAATPdDNJnrSwoCanyon.comSend a message to Rick
![]() A Tip A Day feed
A Tip A Day feed
![]() Point Lookout weekly feed
Point Lookout weekly feed
 My blog, Technical Debt for Policymakers, offers
resources, insights, and conversations of interest to policymakers who are concerned with managing
technical debt within their organizations. Get the millstone of technical debt off the neck of your
organization!
My blog, Technical Debt for Policymakers, offers
resources, insights, and conversations of interest to policymakers who are concerned with managing
technical debt within their organizations. Get the millstone of technical debt off the neck of your
organization!