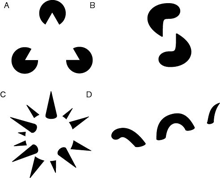
Perceptual illusions resulting from reification. Reification also occurs in human perceptual systems. In these visual examples, we can "see" objects that aren't actually depicted in the images. In A, we see a triangle; in B, a rectangle; in C, a sphere; and in D, a plane.
The processes involved in visual reification are no doubt distinct from the reifications of performance management, but these illustrations provide powerful insight into the effects of reification when dealing with constructs. When we make reification errors, whether in perception or in logic, our experience of the world departs from its reality.
Image by Albert kok courtesy Wikimedia.
To deal with abstract concepts as if they were concrete things is to commit the reification error. [Levy 1997] For example, it's perfectly legitimate (though probably pointless) to measure an employee's average weight over the first two quarters of a fiscal year. But to believe that we can measure an employee's performance over those same two quarters is to commit the reification error.
Performance isn't a real thing — it's a construct. Since it cannot be directly measured, the results of measurements can vary with the approach of the measurer. There is little justification for preferring, in general, any particular kind of measure of any one aspect of performance.
For example, in call centers, a common performance measure is the number of calls handled. Since calls aren't concrete objects, we cannot actually measure their properties as we would measure the weight of a 100-pound sack of flour. Consequently, the effort and expertise required to handle a given call can vary significantly. When there's significant variability among calls, the mere number of calls handled is a poor measure of performance.
A useful indicator of the risk of committing the reification error is the level of abstraction of the entity in question. Here are some examples of abstract concepts relating to performance management, and ways to commit the reification error when dealing with them.
- Demonstrates high levels of motivation
- Motivation isn't a real thing. It cannot be measured directly. We can comment on specific behaviors as indicators of motivation, but since those behaviors are strongly context-dependent, such comments are usually of less value than we believe.
- Works well with others
- Since how well one works with others Since how well one works
with others isn't a real
thing, it cannot be measured
in any absolute senseisn't a real thing, it cannot be measured in any absolute sense. But in this case something even more confusing is afoot: the effectiveness of any pairing of employees is beyond the control of either one. - Recommendations are consistent with management goals
- The degree of consistency between an employee's recommendations and management goals is, of course, not a real thing. To believe that measuring it yields repeatable, meaningful results is to commit the reification error. Moreover, even when recommendations are not consistent with management goals, the elucidation of those goals is management's responsibility. How clearly those goals were enunciated, and how correct and consistent they are, can determine the alignment between those goals and any employee's recommendations.
- Demonstrates consistent, effective leadership
- This is yet another concept that is not a real, measurable thing. Moreover, as in "Works well with others," this component of performance is not under the full control of the performer, because the followers, too, have a say in the effectiveness of the leadership.
Reification is itself a construct. To measure the prevalence of reification errors in a performance management program would be to risk committing a reification error. ![]() Top
Top ![]() Next Issue
Next Issue
Are your projects always (or almost always) late and over budget? Are your project teams plagued by turnover, burnout, and high defect rates? Turn your culture around. Read 52 Tips for Leaders of Project-Oriented Organizations, filled with tips and techniques for organizational leaders. Order Now!
Footnotes
Your comments are welcome
Would you like to see your comments posted here? rbrenaXXxGCwVgbgLZDuRner@ChacDjdMAATPdDNJnrSwoCanyon.comSend me your comments by email, or by Web form.About Point Lookout
 Thank you for reading this article. I hope you enjoyed it and
found it useful, and that you'll consider recommending it to a friend.
Thank you for reading this article. I hope you enjoyed it and
found it useful, and that you'll consider recommending it to a friend.
This article in its entirety was written by a human being. No machine intelligence was involved in any way.
Point Lookout is a free weekly email newsletter. Browse the archive of past issues. Subscribe for free.
Support Point Lookout by joining the Friends of Point Lookout, as an individual or as an organization.
Do you face a complex interpersonal situation? Send it in, anonymously if you like, and I'll give you my two cents.
Related articles
More articles on Personal, Team, and Organizational Effectiveness:
 Please Remove My Appendix
Please Remove My Appendix- When an organization is experiencing problems with conflict, "pushback," or "blowback,"
managers often hire trainers to present programs on helpful topics. But self-diagnosis can be risky.
Often, there are more direct and focused options that can help more and cost less.
 Completism
Completism- Completism is the desire to create or acquire a complete set of something. In our personal lives, it
drives collectors to pay high prices for rare items that "complete the set." In business it
drives us to squander our resources in surprising ways.
 Mitigating Outsourcing Risks: II
Mitigating Outsourcing Risks: II- Outsourcing internal processes exposes the organization to a special class of risks that are peculiar
to the outsourcing relationship. Here is Part II of a discussion of what some of those risks are and
what can we do about them.
 The Deck Chairs of the Titanic: Task Duration
The Deck Chairs of the Titanic: Task Duration- Much of what we call work is as futile and irrelevant as rearranging the deck chairs of the
Titanic. We continue our exploration of futile and irrelevant work, this time emphasizing behaviors
that extend task duration.
 Pseudo-Collaborations
Pseudo-Collaborations- Most workplace collaborations produce results of value. But some collaborations — pseudo-collaborations
— are inherently incapable of producing value, due, in part, to performance management systems,
lack of authority, or lack of access to information.
See also Personal, Team, and Organizational Effectiveness for more related articles.
Forthcoming issues of Point Lookout
 Coming October 1: On the Risks of Obscuring Ignorance
Coming October 1: On the Risks of Obscuring Ignorance- A common dilemma in knowledge-based organizations: ask for an explanation, or "fake it" until you can somehow figure it out. The choice between admitting your own ignorance or obscuring it can be a difficult one. It has consequences for both the choice-maker and the organization. Available here and by RSS on October 1.
 And on October 8: Responding to Workplace Bullying
And on October 8: Responding to Workplace Bullying- Effective responses to bullying sometimes include "pushback tactics" that can deter perpetrators from further bullying. Because perpetrators use some of these same tactics, some people have difficulty employing them. But the need is real. Pushing back works. Available here and by RSS on October 8.
Coaching services
I offer email and telephone coaching at both corporate and individual rates. Contact Rick for details at rbrenaXXxGCwVgbgLZDuRner@ChacDjdMAATPdDNJnrSwoCanyon.com or (650) 787-6475, or toll-free in the continental US at (866) 378-5470.
Get the ebook!
Past issues of Point Lookout are available in six ebooks:
- Get 2001-2 in Geese Don't Land on Twigs (PDF, )
- Get 2003-4 in Why Dogs Wag (PDF, )
- Get 2005-6 in Loopy Things We Do (PDF, )
- Get 2007-8 in Things We Believe That Maybe Aren't So True (PDF, )
- Get 2009-10 in The Questions Not Asked (PDF, )
- Get all of the first twelve years (2001-2012) in The Collected Issues of Point Lookout (PDF, )
Are you a writer, editor or publisher on deadline? Are you looking for an article that will get people talking and get compliments flying your way? You can have 500-1000 words in your inbox in one hour. License any article from this Web site. More info
Follow Rick
Recommend this issue to a friend
Send an email message to a friend
rbrenaXXxGCwVgbgLZDuRner@ChacDjdMAATPdDNJnrSwoCanyon.comSend a message to Rick
![]() A Tip A Day feed
A Tip A Day feed
![]() Point Lookout weekly feed
Point Lookout weekly feed
 My blog, Technical Debt for Policymakers, offers
resources, insights, and conversations of interest to policymakers who are concerned with managing
technical debt within their organizations. Get the millstone of technical debt off the neck of your
organization!
My blog, Technical Debt for Policymakers, offers
resources, insights, and conversations of interest to policymakers who are concerned with managing
technical debt within their organizations. Get the millstone of technical debt off the neck of your
organization!