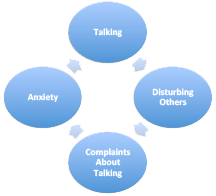
A diagram illustrating how, in some cases, compulsive talking leads to increased compulsion to talk. As anxiety increases, there is an increased urge to talk. This increases the annoyance to others, who then are more likely to complain about the incessant talking. This, in turn raises the talker's level of anxiety, increasing the urge to talk.
Some people talk way more than we'd like them to. They talk incessantly. In extreme cases, we wonder how someone can talk so much and say so little. Getting a word in can be difficult, which is bad enough, but typically, we don't even want to participate in the so-called conversation. We just want these people to disappear, so we can get back to work, or just think, or have a real conversation with someone else.
What can you do about such people? How can you tell them that their behavior is unacceptable, without destroying the relationship?
Some call these people talkaholics, a word that's derived (by extension) from the term alcoholic. But the name is misleading, because alcoholism is a substance addiction, and "talkaholism" is probably a behavioral addiction, like gambling. I say "probably" because, as of this writing, the only behavioral addiction officially recognized by the psychology and psychiatry communities is gambling. Because substance ingestion isn't involved in talkaholism, I prefer the term compulsive talking or talking addiction.
We do have choices when dealing with compulsive talkers, but because the choices are somewhat unsatisfactory, the most severe challenge we face when dealing with compulsive talkers at work is accepting our own limitations. And the path to that acceptance begins with understanding the fundamentals of behavioral addiction.
Behavioral addiction Behavioral addiction involves a
compulsion to repeat a behavior
in spite of its severe negative
consequences to the individualinvolves a compulsion to repeat a behavior in spite of its severe negative consequences to the individual. The compulsion arises from re-enforcing and rewarding stimuli that are direct results of the behavior. The reward is psychic — that is, the individual interprets at least some consequences of the behavior as a positive experience. Repeatedly receiving the reward induces the person to repeat the behavior that generated the reward. Over time, the individual can become so focused on obtaining the reward by repeating the behavior, that the behavior can become the center of the individual's daily life.
For example, some people talk to calm themselves when they experience anxiety. When they feel anxious, they talk, and they feel better. The next time they feel anxious, they're a little more likely to talk. Soon, they engage in talking whenever they anticipate anxiety. And then the problem can become severe, especially if they develop anxiousness about talking too much. If that happens, they can enter a regime in which talking continuously is the only way they can gain any sense of relief from anxiety.
That's just one example of the many ways people can become addicted to talking. It's easy to see in that example why trying to convince a compulsive talker to "stop it" is a fool's errand. The attempt to convince the addict to abandon the addiction can itself intensify the addiction. So if we can't convince — and indeed ought not even try to convince — the compulsive talker to change, what can we do? We'll tackle that question next time. ![]() Next issue in this series
Next issue in this series ![]() Top
Top ![]() Next Issue
Next Issue
Are you fed up with tense, explosive meetings? Are you or a colleague the target of a bully? Destructive conflict can ruin organizations. But if we believe that all conflict is destructive, and that we can somehow eliminate conflict, or that conflict is an enemy of productivity, then we're in conflict with Conflict itself. Read 101 Tips for Managing Conflict to learn how to make peace with conflict and make it an organizational asset. Order Now!
Your comments are welcome
Would you like to see your comments posted here? rbrenaXXxGCwVgbgLZDuRner@ChacDjdMAATPdDNJnrSwoCanyon.comSend me your comments by email, or by Web form.About Point Lookout
 Thank you for reading this article. I hope you enjoyed it and
found it useful, and that you'll consider recommending it to a friend.
Thank you for reading this article. I hope you enjoyed it and
found it useful, and that you'll consider recommending it to a friend.
This article in its entirety was written by a human being. No machine intelligence was involved in any way.
Point Lookout is a free weekly email newsletter. Browse the archive of past issues. Subscribe for free.
Support Point Lookout by joining the Friends of Point Lookout, as an individual or as an organization.
Do you face a complex interpersonal situation? Send it in, anonymously if you like, and I'll give you my two cents.
Related articles
More articles on Conflict Management:
 Impasses in Group Decision Making: II
Impasses in Group Decision Making: II- When groups can't reach agreement on all aspects of an issue, the tactics of some members can actually
exacerbate disagreement. Here's Part II of an exploration of impasses, emphasizing two of the more toxic
tactics.
 Social Isolation and Workplace Bullying
Social Isolation and Workplace Bullying- Social isolation is a tactic widely used by workplace bullies. What is it? How do bullies use it? Why
do bullies use it? What can targets do about it?
 Managing Dissent Risk
Managing Dissent Risk- In group decision making, dissent risk is the risk that dissents about important decisions will be rejected
without due consideration. As a result, group decision quality can suffer, and some groups will actually
eject dissenters. How can we manage dissent risk?
 Strategy for Targets of Verbal Abuse
Strategy for Targets of Verbal Abuse- Many targets of verbal abuse at work believe that they have just two strategic options: find a new job,
or accept the abuse. In some cases, they're correct. But not always.
 Quasi-Narcissistic Quasi-Subordinates
Quasi-Narcissistic Quasi-Subordinates- One troublesome kind of workplace collaboration includes those that combine people of varied professions
and ranks for a specific short-term mission. Many work well, but when one of the group members displays
quasi-narcissistic behaviors, trouble looms.
See also Conflict Management for more related articles.
Forthcoming issues of Point Lookout
 Coming October 1: On the Risks of Obscuring Ignorance
Coming October 1: On the Risks of Obscuring Ignorance- When people hide their ignorance of concepts fundamental to understanding the issues at hand, they expose their teams and organizations to a risk of making wrong decisions. The organizational costs of the consequences of those decisions can be unlimited. Available here and by RSS on October 1.
 And on October 8: Responding to Workplace Bullying
And on October 8: Responding to Workplace Bullying- Effective responses to bullying sometimes include "pushback tactics" that can deter perpetrators from further bullying. Because perpetrators use some of these same tactics, some people have difficulty employing them. But the need is real. Pushing back works. Available here and by RSS on October 8.
Coaching services
I offer email and telephone coaching at both corporate and individual rates. Contact Rick for details at rbrenaXXxGCwVgbgLZDuRner@ChacDjdMAATPdDNJnrSwoCanyon.com or (650) 787-6475, or toll-free in the continental US at (866) 378-5470.
Get the ebook!
Past issues of Point Lookout are available in six ebooks:
- Get 2001-2 in Geese Don't Land on Twigs (PDF, )
- Get 2003-4 in Why Dogs Wag (PDF, )
- Get 2005-6 in Loopy Things We Do (PDF, )
- Get 2007-8 in Things We Believe That Maybe Aren't So True (PDF, )
- Get 2009-10 in The Questions Not Asked (PDF, )
- Get all of the first twelve years (2001-2012) in The Collected Issues of Point Lookout (PDF, )
Are you a writer, editor or publisher on deadline? Are you looking for an article that will get people talking and get compliments flying your way? You can have 500-1000 words in your inbox in one hour. License any article from this Web site. More info
Follow Rick
Recommend this issue to a friend
Send an email message to a friend
rbrenaXXxGCwVgbgLZDuRner@ChacDjdMAATPdDNJnrSwoCanyon.comSend a message to Rick
![]() A Tip A Day feed
A Tip A Day feed
![]() Point Lookout weekly feed
Point Lookout weekly feed
 My blog, Technical Debt for Policymakers, offers
resources, insights, and conversations of interest to policymakers who are concerned with managing
technical debt within their organizations. Get the millstone of technical debt off the neck of your
organization!
My blog, Technical Debt for Policymakers, offers
resources, insights, and conversations of interest to policymakers who are concerned with managing
technical debt within their organizations. Get the millstone of technical debt off the neck of your
organization!