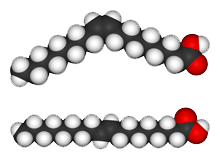
The molecular structure of Oleic Acid (a cis fat, top), and Elaidic Acid (a trans fat, bottom). The two fats have identical numbers of carbon atoms (black), hydrogen atoms (white) and oxygen atoms (red). The numbers of different bond types are also identical. The difference between the two is the placement of the carbon-carbon double bonds near the middle of the chains. In the trans fat version (Elaidic Acid, bottom), the carbon-carbon double bonds are across from each other (hence the name trans fat). In the cis fat version, the Oleic Acid, the carbon-carbon double bonds are adjacent to each other, which causes a bend in the chain at that point. (The prefix cis is from Latin. It means "on this side").
The molecules of the trans isomer are able to pack tightly together to form a solid at temperatures of the human body and slightly above. The molecules of the cis isomer aren't able to do so. They are liquids. This solidification property makes the trans fat an attractive ingredient for foods, because it extends shelf life by preventing rancidity. It also makes the trans fat a deadly ingredient in food, because it solidifies and collects on arterial walls, contributing to heart disease. Photos courtesy Wikipedia.
It's often difficult to detect a lie, but detecting lies can be much easier. Although spotting a single instance of a misleading statement can be difficult, we can often detect deceptions that might otherwise escape our notice if they're part of a series of statements offered over a period of time. One form that facilitates this scenario is the interview.
The term interview connotes a friendly question-and-answer format that we might encounter in print media or broadcast media. But the term also applies to a nonaccusatory question-and-answer session during or after presentations at meetings, or in a one-on-one meeting with one's supervisor, or any of dozens of other situations at work. Interviews are distinguished from interrogations, which are clearly accusatory.
Here's Part III of our little catalog of indicators that suggest the handiwork of a deceiver, emphasizing techniques that apply during interviews. See "Some Truths About Lies: I," Point Lookout for August 4, 2004, for more.
- Unpleasantness, defensiveness, or intimidation
- Although many follow-up questions are motivated by innocent confusion or a search for clarity, some deceivers experience follow-up questions as challenges to the deceiver's claims. To prevent further follow-up questions, deceivers who fear that their deceptions aren't working sometimes express resentment or anger in response to follow-up questions. Rarely are these emotional displays real in the conventional sense. The deceivers are just using intimidation as a diversion to prevent further probing.
- Deceivers who use intimidation, anger, sarcasm, or other means of deterring further questioning are at best failing to cooperate with the interviewer; at worst, they're concealing something important.
- That can't be it; it's too small
- Deceivers intent on discrediting evidence of errors, negligence, or wrongdoing sometimes assert that evidence is invalid because it's inconclusive on its own, even when it is valid as part of a complete pattern of evidence, or when it typifies incidents that have occurred numerous times. For example, consuming one gram of trans fat doesn't cause coronary artery disease. But consuming one gram per day for thirty years probably would.
- Evidence dismissed by the deceiver prematurely as insufficient could indicate a desire to conceal a larger body of damning evidence. During the interview, take note of repeated use of this technique.
- An answer for everything
- When interviewers When interviewers probe for more
complete disclosure of deceivers'
positions, some deceivers have
exculpatory responses for
absolutely every questionprobe for more complete disclosure of deceivers' positions, some deceivers have exculpatory responses for absolutely every question. Such a 100% performance isn't typical outside the realm of deception, because most people have only incomplete knowledge of any given situation. - More important, though, deceivers know that they're deceiving. Some are a little frightened about it. They tend to compensate by presenting stories without holes. But since some highly sophisticated deceivers know that ironclad stories are the mark of the deceiver, they do include some (unimportant) holes now and then.
We'll continue next time with more techniques for detecting lies using the interview. ![]() First issue in this series
First issue in this series ![]() Next issue in this series
Next issue in this series ![]() Top
Top ![]() Next Issue
Next Issue
Is every other day a tense, anxious, angry misery as you watch people around you, who couldn't even think their way through a game of Jacks, win at workplace politics and steal the credit and glory for just about everyone's best work including yours? Read 303 Secrets of Workplace Politics, filled with tips and techniques for succeeding in workplace politics. More info
Your comments are welcome
Would you like to see your comments posted here? rbrenaXXxGCwVgbgLZDuRner@ChacDjdMAATPdDNJnrSwoCanyon.comSend me your comments by email, or by Web form.About Point Lookout
 Thank you for reading this article. I hope you enjoyed it and
found it useful, and that you'll consider recommending it to a friend.
Thank you for reading this article. I hope you enjoyed it and
found it useful, and that you'll consider recommending it to a friend.
This article in its entirety was written by a human being. No machine intelligence was involved in any way.
Point Lookout is a free weekly email newsletter. Browse the archive of past issues. Subscribe for free.
Support Point Lookout by joining the Friends of Point Lookout, as an individual or as an organization.
Do you face a complex interpersonal situation? Send it in, anonymously if you like, and I'll give you my two cents.
Related articles
More articles on Ethics at Work:
 It Might Be Legal, but It's Unethical
It Might Be Legal, but It's Unethical- Now that CEOs will be held personally accountable for statements they make about their organizations,
we can all expect to be held to higher standards of professional ethics. Some professions have formal
codes of ethics, but most don't. What ethical principles guide you?
 Nonworkplace Politics
Nonworkplace Politics- When we bring national or local political issues into the workplace — especially the divisive
issues — we risk disrupting our relationships, our projects, and the company itself.
 Approval Ploys
Approval Ploys- If you approve or evaluate proposals or requests made by others, you've probably noticed patterns approval
seekers use to enhance their success rates. Here are some tactics approval seekers use.
 Telephonic Deceptions: I
Telephonic Deceptions: I- People have been deceiving each other at work since the invention of work. Nowadays, with telephones
ever-present, telephonic deceptions are becoming more creative. Here's Part I of a handy guide for telephonic
self-defense.
 Availability and Self-Assessments
Availability and Self-Assessments- In many organizations, employees develop self-assessments as a part of the performance review process.
Because of a little-known effect related to the Availability Heuristic, these self-assessments can be
biased against the employee.
See also Ethics at Work for more related articles.
Forthcoming issues of Point Lookout
 Coming October 1: On the Risks of Obscuring Ignorance
Coming October 1: On the Risks of Obscuring Ignorance- A common dilemma in knowledge-based organizations: ask for an explanation, or "fake it" until you can somehow figure it out. The choice between admitting your own ignorance or obscuring it can be a difficult one. It has consequences for both the choice-maker and the organization. Available here and by RSS on October 1.
 And on October 8: Responding to Workplace Bullying
And on October 8: Responding to Workplace Bullying- Effective responses to bullying sometimes include "pushback tactics" that can deter perpetrators from further bullying. Because perpetrators use some of these same tactics, some people have difficulty employing them. But the need is real. Pushing back works. Available here and by RSS on October 8.
Coaching services
I offer email and telephone coaching at both corporate and individual rates. Contact Rick for details at rbrenaXXxGCwVgbgLZDuRner@ChacDjdMAATPdDNJnrSwoCanyon.com or (650) 787-6475, or toll-free in the continental US at (866) 378-5470.
Get the ebook!
Past issues of Point Lookout are available in six ebooks:
- Get 2001-2 in Geese Don't Land on Twigs (PDF, )
- Get 2003-4 in Why Dogs Wag (PDF, )
- Get 2005-6 in Loopy Things We Do (PDF, )
- Get 2007-8 in Things We Believe That Maybe Aren't So True (PDF, )
- Get 2009-10 in The Questions Not Asked (PDF, )
- Get all of the first twelve years (2001-2012) in The Collected Issues of Point Lookout (PDF, )
Are you a writer, editor or publisher on deadline? Are you looking for an article that will get people talking and get compliments flying your way? You can have 500-1000 words in your inbox in one hour. License any article from this Web site. More info
Follow Rick
Recommend this issue to a friend
Send an email message to a friend
rbrenaXXxGCwVgbgLZDuRner@ChacDjdMAATPdDNJnrSwoCanyon.comSend a message to Rick
![]() A Tip A Day feed
A Tip A Day feed
![]() Point Lookout weekly feed
Point Lookout weekly feed
 My blog, Technical Debt for Policymakers, offers
resources, insights, and conversations of interest to policymakers who are concerned with managing
technical debt within their organizations. Get the millstone of technical debt off the neck of your
organization!
My blog, Technical Debt for Policymakers, offers
resources, insights, and conversations of interest to policymakers who are concerned with managing
technical debt within their organizations. Get the millstone of technical debt off the neck of your
organization!