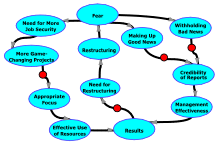
A diagram of effects illustrating the first two loops of the three loops of the Restructuring-Fear Cycle described here. View a larger image. The turquoise ovals represent quantitative amounts. For example, the oval labeled "Need for Restructuring" represents the perceived need for a restructuring event. The oval labeled "Credibility of Reports" represents the perceived credibility of reports about work underway in an organization in which people fear the consequences of reporting bad news honestly, or fear the consequences of failing to report good news with sufficient frequency. An arrow connecting one oval to another indicates that an increase in the first quantity contributes to an increase in the quantity it points to. Thus, an increase in Credibility of Reports contributes to an increase in Management Effectiveness. An arrow bearing a red circle indicates a negative relationship. Thus, an increase in Withholding Bad News contributes to a decrease in Credibility of Reports.
If any loop of this diagram contains an even number of red circles, such as 0, 2, 4, and so on, then it rerpresents a positive feedback loop, and the quantities in that loop can "run away" unless Management (or the laws of economics, psychology, or physics) somehow intervene. This diagram, which illustrates only some of the phenomena affecting the Need for Restructuring, shows that there are two pathways that can cause a runaway need for restructuring.
The two loops shown correspond to Credibility Erosion and Getting Things in Under the Wire. Left as an exercise for you is the third mechanism, Roster Padding.
Last time we began exploring the Restructuring-Fear Cycle, which shows how the fear induced by restructuring can create a need for more restructuring. In effect, organizations can become addicted to restructuring. Here's Part II of our exploration.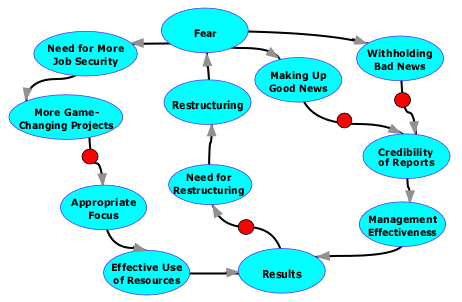
- Credibility erosion
- When employees notice a pattern of restructuring, many assume that their own performance, and that of their business unit, will affect decisions about their job security. Correct or not, this speculation can lead to withholding bad news, or worse, creating fictitious good news. As status reports travel up the management chain, some recipients, anticipating this shading of the truth, doubt the veracity of the reports.
- When what we say to each other becomes unreliable, managing the organization becomes truly difficult. Enterprise performance is at risk. In this way, restructuring events can degrade enterprise performance, which increases the need for further restructuring. Top-to-bottom management replacement, as in a spin-off or acquisition, is sometimes the only way to end this cycle.
- Getting things in under the wire
- Among managers who recognize that further restructuring lies ahead are those who undertake so-called game-changing projects that promise a brighter future. They're hoping, in part, to enhance their own job security. Because they typically believe that the opportunity for initiating new projects is short-lived, they tend to oversell the attractiveness of their initiatives by representing them as better developed, lower-risk, more important, and more urgent than they really are.
- This dynamic can lead the enterprise to undertake too many new efforts, many of them too disconnected from its core mission. The problems inherent in development are often understated, and the downstream costs of supporting new offerings are often underestimated. Many of these efforts come to nothing. The resources invested are wasted, which leads to enhanced necessity for further restructuring.
- Roster padding
- Within most Among managers who recognize that
further restructuring lies ahead
are those who undertake so-called
game-changing projects that
promise a brighter futureenterprises, we can usually find a most-politically-powerful entity — a brand, a business unit, or a constellation of smaller entities exploiting a single market position. To employees who fear job loss as a consequence of restructuring, the most-politically-powerful elements seem like possible havens of job security. - Managers within the politically powerful elements thus sometimes experience a flux of jobs seekers from other business units. Before the restructuring began, some of these people would not have been obtainable at the rates being offered, or not obtainable at all. Some managers succumb to the temptation to make internal hires. When external hiring is frozen, but internal transfers are still permitted, politically powerful entities can find themselves bloated with employees and projects. Their expenses climb, and soon there is need for yet another round of restructuring.
I could go on, but I think you get the idea. Restructuring breeds fear, fear lowers margins, and the cycle continues. ![]() First issue in this series
First issue in this series ![]() Top
Top ![]() Next Issue
Next Issue
Are your projects always (or almost always) late and over budget? Are your project teams plagued by turnover, burnout, and high defect rates? Turn your culture around. Read 52 Tips for Leaders of Project-Oriented Organizations, filled with tips and techniques for organizational leaders. Order Now!
[1]Weinberg, Gerald M. Quality Software Management Volume 1: Systems Thinking. New York: Dorset House, 1989. Order from Amazon.com
Your comments are welcome
Would you like to see your comments posted here? rbrenaXXxGCwVgbgLZDuRner@ChacDjdMAATPdDNJnrSwoCanyon.comSend me your comments by email, or by Web form.About Point Lookout
 Thank you for reading this article. I hope you enjoyed it and
found it useful, and that you'll consider recommending it to a friend.
Thank you for reading this article. I hope you enjoyed it and
found it useful, and that you'll consider recommending it to a friend.
This article in its entirety was written by a human being. No machine intelligence was involved in any way.
Point Lookout is a free weekly email newsletter. Browse the archive of past issues. Subscribe for free.
Support Point Lookout by joining the Friends of Point Lookout, as an individual or as an organization.
Do you face a complex interpersonal situation? Send it in, anonymously if you like, and I'll give you my two cents.
Related articles
More articles on Emotions at Work:
 Email Happens
Email Happens- Email is a wonderful medium for some communications, and extremely dangerous for others. What are its
limitations? How can we use email safely?
 Some Subtleties of ad hominem Attacks
Some Subtleties of ad hominem Attacks- Groups sometimes make mistakes based on faulty reasoning used in their debates. One source of faulty
reasoning is the ad hominem attack. Here are some insights that help groups recognize and avoid this
class of errors.
 Not Really Part of the Team: II
Not Really Part of the Team: II- When some team members hang back, declining to show initiative, we tend to overlook the possibility
that their behavior is a response to something happening within or around the team. Too often we hold
responsible the person who's hanging back. What other explanations are possible?
 More Things I've Learned Along the Way
More Things I've Learned Along the Way- Some entries from my personal collection of useful insights.
 Directed Attention Fatigue
Directed Attention Fatigue- Humans have a limited capacity to concentrate attention on thought-intensive tasks. After a time, we
must rest and renew. Most brainwork jobs aren't designed with this in mind.
See also Emotions at Work for more related articles.
Forthcoming issues of Point Lookout
 Coming October 1: On the Risks of Obscuring Ignorance
Coming October 1: On the Risks of Obscuring Ignorance- A common dilemma in knowledge-based organizations: ask for an explanation, or "fake it" until you can somehow figure it out. The choice between admitting your own ignorance or obscuring it can be a difficult one. It has consequences for both the choice-maker and the organization. Available here and by RSS on October 1.
 And on October 8: Responding to Workplace Bullying
And on October 8: Responding to Workplace Bullying- Effective responses to bullying sometimes include "pushback tactics" that can deter perpetrators from further bullying. Because perpetrators use some of these same tactics, some people have difficulty employing them. But the need is real. Pushing back works. Available here and by RSS on October 8.
Coaching services
I offer email and telephone coaching at both corporate and individual rates. Contact Rick for details at rbrenaXXxGCwVgbgLZDuRner@ChacDjdMAATPdDNJnrSwoCanyon.com or (650) 787-6475, or toll-free in the continental US at (866) 378-5470.
Get the ebook!
Past issues of Point Lookout are available in six ebooks:
- Get 2001-2 in Geese Don't Land on Twigs (PDF, )
- Get 2003-4 in Why Dogs Wag (PDF, )
- Get 2005-6 in Loopy Things We Do (PDF, )
- Get 2007-8 in Things We Believe That Maybe Aren't So True (PDF, )
- Get 2009-10 in The Questions Not Asked (PDF, )
- Get all of the first twelve years (2001-2012) in The Collected Issues of Point Lookout (PDF, )
Are you a writer, editor or publisher on deadline? Are you looking for an article that will get people talking and get compliments flying your way? You can have 500-1000 words in your inbox in one hour. License any article from this Web site. More info
Follow Rick
Recommend this issue to a friend
Send an email message to a friend
rbrenaXXxGCwVgbgLZDuRner@ChacDjdMAATPdDNJnrSwoCanyon.comSend a message to Rick
![]() A Tip A Day feed
A Tip A Day feed
![]() Point Lookout weekly feed
Point Lookout weekly feed
 My blog, Technical Debt for Policymakers, offers
resources, insights, and conversations of interest to policymakers who are concerned with managing
technical debt within their organizations. Get the millstone of technical debt off the neck of your
organization!
My blog, Technical Debt for Policymakers, offers
resources, insights, and conversations of interest to policymakers who are concerned with managing
technical debt within their organizations. Get the millstone of technical debt off the neck of your
organization!