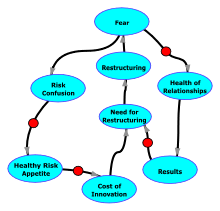
A diagram of effects illustrating these two loops in the Restructuring-Fear Cycle. View a larger image. The turquoise ovals represent quantitative amounts. For example the oval labeled "Need for Restructuring" represents a measure of the perceived need for a restructuring exercise. The oval labeled "Health of Relationships" represents a measure of the relative health of interpersonal relationships in the organization. An arrow connecting one oval to another indicates that an increase in the first quantity contributes to an increase in the quantity it points to. Thus, an increase in Health of Relationships contributes to an increase in Results. An arrow bearing a red circle indicates a negative relationship. Thus, an increase in Risk Confusion contributes to a decrease in Healthy Risk Appetite.
Following the arrows around any loop in such a diagram, if we encounter an even number of red circles, such as 0, 2, 4, and so on, then that loop represents a positive feedback loop, and the quantities in that loop can "run away" unless Management (or the laws of economics, psychology, or physics) somehow intervene. This diagram, which illustrates only some of the phenomena affecting the Need for Restructuring, has two such loops, which implies that there are two pathways that can cause a runaway need for restructuring.
Decisions about restructuring usually depend on models that show how different approaches might affect the enterprise, by projecting the values of organizational attributes such as net income, market share, or shareholder value. Although these projections rarely include attributes like employee anxiety or fear, such factors are truly important. They help to determine productivity, voluntary turnover, the workload of the people in Human Resources, and many of the attributes that the experts do model, albeit indirectly.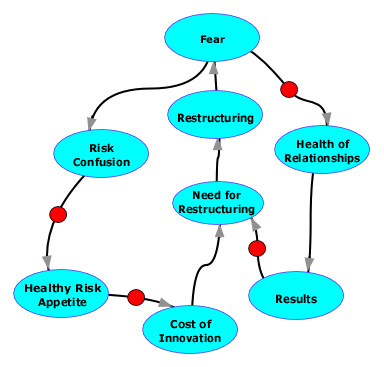
Most important, restructuring-induced fear can create a need for future restructuring, through a variety of paths, some of which are subtle and rarely identified. Here's Part I of an exploration of some of the less obvious mechanisms by which restructuring-induced fear creates a need for future restructuring. Refer to the accompanying diagram of effects, which displays these dynamics graphically. [Weinberg 1989]
- Degraded and disrupted relationships
- When we relocate people, eliminate positions, or merely change reporting structures, we disrupt relationships between people. Those who formerly relied on each other for advice, instruction, or services must sometimes find new contacts. Even the relationships that aren't totally eliminated can be degraded by restructuring-induced fear, in the form of competitive attitudes that can take hold when people come to believe that further restructuring is possible, and that everyone is in competition for a declining number of jobs.
- Although relationships between and among employees are valuable organizational assets, the value of these assets doesn't appear on financial statements. Unaware of the amount of these assets lost to restructuring, the depressive effects on results seem surprising to planners. The unexpectedly disappointing results can sometimes lead to further restructuring.
- Risk aversion
- When people believe that their When people believe that
their jobs are at risk,
their appetite for risk
in general declinesjobs are at risk, their appetite for risk in general declines. In effect, some people have difficulty keeping separate their own personal risk profile and the risk profile associated with their job responsibilities. This can affect the necessarily subjective judgments people make as part of their responsibilities, which creates a risk aversive approach to operating the enterprise. - After experiencing several serial restructuring events, people in organizations that formerly had a healthy approach to risk can find themselves being overly conservative in their strategies and tactics, because they have begun to confuse their own personal risk experience with the risk experience of the organization. In this way, the organization can become so risk averse that it is no longer capable of accepting the levels of well-managed risk that are so necessary in today's market environments. These organizations then find that they can innovate only by acquiring innovative organizations, which is an expensive method for attaining market leadership. The resulting high costs and low yields sometimes lead to further need for restructuring.
Next time we'll explore three more pathways by which restructuring-induced fear leads to restructuring addiction. ![]() Next issue in this series
Next issue in this series ![]() Top
Top ![]() Next Issue
Next Issue
Are your projects always (or almost always) late and over budget? Are your project teams plagued by turnover, burnout, and high defect rates? Turn your culture around. Read 52 Tips for Leaders of Project-Oriented Organizations, filled with tips and techniques for organizational leaders. Order Now!
Footnotes
Your comments are welcome
Would you like to see your comments posted here? rbrenaXXxGCwVgbgLZDuRner@ChacDjdMAATPdDNJnrSwoCanyon.comSend me your comments by email, or by Web form.About Point Lookout
 Thank you for reading this article. I hope you enjoyed it and
found it useful, and that you'll consider recommending it to a friend.
Thank you for reading this article. I hope you enjoyed it and
found it useful, and that you'll consider recommending it to a friend.
This article in its entirety was written by a human being. No machine intelligence was involved in any way.
Point Lookout is a free weekly email newsletter. Browse the archive of past issues. Subscribe for free.
Support Point Lookout by joining the Friends of Point Lookout, as an individual or as an organization.
Do you face a complex interpersonal situation? Send it in, anonymously if you like, and I'll give you my two cents.
Related articles
More articles on Emotions at Work:
 Blind Agendas
Blind Agendas- Effective meetings have agendas. But even if a meeting has an agenda, the hidden agendas of participants
can cause trouble. Another source of trouble, less frequently recognized, is the blind agenda.
 Sixteen Overload Haiku
Sixteen Overload Haiku- Most of us have some experience of being overloaded and overworked. Many of us have forgotten what it
is not to be overloaded. Here's a contemplation of the state of overload.
 On Advice and Responsibility
On Advice and Responsibility- Being asked for advice can be an affirming experience, but actually giving advice can sometimes entail
risk. How can this happen, and what choices do we have?
 Toxic Conflict in Teams: Attacks
Toxic Conflict in Teams: Attacks- In toxic conflict, people try to resolve their differences by eliminating each other's ability to provide
opposition. In the early stages of toxic conflict, the attacks often escape notice. Here's a catalog
of covert attack tactics.
 Heart with Mind
Heart with Mind- We say people have "heart" when they continue to pursue a goal despite obstacles that would
discourage almost everyone. We say that people are stubborn when they continue to pursue a goal that
we regard as unachievable. What are our choices when achieving the goal is difficult?
See also Emotions at Work for more related articles.
Forthcoming issues of Point Lookout
 Coming October 1: On the Risks of Obscuring Ignorance
Coming October 1: On the Risks of Obscuring Ignorance- When people hide their ignorance of concepts fundamental to understanding the issues at hand, they expose their teams and organizations to a risk of making wrong decisions. The organizational costs of the consequences of those decisions can be unlimited. Available here and by RSS on October 1.
 And on October 8: Responding to Workplace Bullying
And on October 8: Responding to Workplace Bullying- Effective responses to bullying sometimes include "pushback tactics" that can deter perpetrators from further bullying. Because perpetrators use some of these same tactics, some people have difficulty employing them. But the need is real. Pushing back works. Available here and by RSS on October 8.
Coaching services
I offer email and telephone coaching at both corporate and individual rates. Contact Rick for details at rbrenaXXxGCwVgbgLZDuRner@ChacDjdMAATPdDNJnrSwoCanyon.com or (650) 787-6475, or toll-free in the continental US at (866) 378-5470.
Get the ebook!
Past issues of Point Lookout are available in six ebooks:
- Get 2001-2 in Geese Don't Land on Twigs (PDF, )
- Get 2003-4 in Why Dogs Wag (PDF, )
- Get 2005-6 in Loopy Things We Do (PDF, )
- Get 2007-8 in Things We Believe That Maybe Aren't So True (PDF, )
- Get 2009-10 in The Questions Not Asked (PDF, )
- Get all of the first twelve years (2001-2012) in The Collected Issues of Point Lookout (PDF, )
Are you a writer, editor or publisher on deadline? Are you looking for an article that will get people talking and get compliments flying your way? You can have 500-1000 words in your inbox in one hour. License any article from this Web site. More info
Follow Rick
Recommend this issue to a friend
Send an email message to a friend
rbrenaXXxGCwVgbgLZDuRner@ChacDjdMAATPdDNJnrSwoCanyon.comSend a message to Rick
![]() A Tip A Day feed
A Tip A Day feed
![]() Point Lookout weekly feed
Point Lookout weekly feed
 My blog, Technical Debt for Policymakers, offers
resources, insights, and conversations of interest to policymakers who are concerned with managing
technical debt within their organizations. Get the millstone of technical debt off the neck of your
organization!
My blog, Technical Debt for Policymakers, offers
resources, insights, and conversations of interest to policymakers who are concerned with managing
technical debt within their organizations. Get the millstone of technical debt off the neck of your
organization!