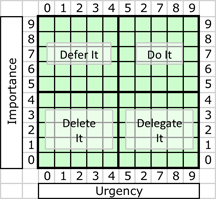
The Eisenhower Matrix of Urgency by Importance. This version enables scoring each dimension from 0 to 9. To discover the range of opinions in a team, each member scores the issue at hand as a coordinate pair [U,I]. The resulting graphic display, or even a simple mean and standard deviation, tells the team its degree of agreement with respect to that issue.
Of the stages of Tuckman's development sequence for small groups, Storming is probably the least suitable for resolving problems. The atmosphere just isn't yet conducive to creative collaboration. More important, though, is that some group members don't yet see themselves as sharing the benefits of having the group find solutions to its problems. [Tuckman 1965] [Tuckman & Jensen 1977] Indeed, some group members can't even agree about what the problems are. Storming is instead a stage for discovering and acknowledging disagreements about problems — for registering objections and expressing disagreement.
And that's a difficult situation to accept. Most of us want to get on with problem solving. We've been taught that solving is progress, and that debating priorities or problem definitions is less than progress. But long experience teaches us that developing consensus about a clean, elegant problem statement is a wise investment. Maybe the wisest. For a brief review of Tuckman and Jensen's model, see "Tuckman's Model and Joint Leadership Teams," Point Lookout for January 18, 2023.
Examples of focal points for the Storming stage
A group has done well if it can convince its members that Storming is a time for airing objections, frustrations, concerns, and troubles. With that in mind, here are ten examples of topics to work on in the stage we call Storming. A word of caution, though: addressing some of these topics might require a level of psychological safety that isn't yet available in your organization.
- Assessing the degree of psychological safety
- We can restate the objective of a Storming stage simply: Uncover the nasty truths. The extent to which this objective is attainable depends on the willingness of group members to speak freely, without fear or favor. And that depends on their sense of psychological safety. There are ways to assess the level of psychological safety using anonymous polling. Knowing how safe the group feels at the outset can help you focus attention where it's needed. For more, see "Contrary Indicators of Psychological Safety: I," Point Lookout for December 13, 2023.
- Training for participating in a Storming stage
- Educate group members as to the benefits of the Storming stage of small group development. The main benefit of the Storming stage is its ability to encourage disclosure of beliefs, biases, agendas, and practices that might threaten the effectiveness of the collaboration — either professionally or personally. For example, Storming is the stage in which we register our discomfort with the group's inability to conduct civil, respectful debate. When the time comes to debate matters of substance, we don't want to be debating how to debate.
- Identifying candidates for group leadership
- Some group members have ambitions to become effective leaders; some have the leader's talent and skills; and some have the leader's disposition. Trouble comes when ambitions, talent, skills, and disposition do not all reside in the same person. In Storming we can assess the ambitions, talent, skills, and dispositions of all members. We can then determine how to begin aligning them.
- Creating and training Curmudgeon Teams
- Long experience teaches us that
developing consensus about a clean,
elegant problem statement is a wise
investment. Maybe the wisest. - The Curmudgeon Team is a subgroup of a larger team. Their job is to strengthen the team's conclusions and results by raising thorny issues that cause the team to examine the path it's about to take, so it can possibly make adjustments. In this way the Curmudgeon Team helps the group avoid dead ends and disasters. More
- Identifying feuds
- Organizational feuds differ from more typical conflict in three ways: (a) the feuding partners repeatedly engage in intense, personal attacks, usually out of all proportion to the issues of the moment; (b) even though the issues of the moment might vary from incident to incident, the feuding partners almost always sort out along the same dividing lines, because the issue of the moment isn't the real issue, which is a matter so highly charged that the feuding partners dare not discuss it openly; and (c) agreement on any issue whatsoever is rare. Feud lifetimes of months or years are typical. Because the issue of the moment isn't the real issue, feuds cannot be resolved in the context of any issue the feuding partners are willing to discuss openly. More
- Identifying feuds-by-proxy
- A feud-by-proxy within a group is a feud in which at least one of the principal feuding partners is absent. Absentees are represented by proxies. Because one of the principals is absent, there is no hope of resolving a feud-by-proxy in the group Storming context. All that can be done for the moment is to recognize the problem (tacitly) and determine the extent of its effects. Possibly the group will need to redesign its task activity around the feud. More
- Identifying bullying behavior
- Workplace bullying is any aggressive behavior, associated with work, and primarily intended to cause physical or psychological harm to others. It creates risk for organizations in several ways, the most costly of which occurs when bullies coerce people into committing to produce what they cannot produce with the resources and time available. In the Storming stage we have opportunities to identify bullying, bullying-by-proxy, and bullying-by-proxy on behalf of an absentee. This last form is the most insidious. If bullying in any form is afoot, all commitments must be considered questionable. An anonymous poll is a good first step toward assessing the risk that bullying might have produced impossible commitments. More
- Conducting premortems
- Premortems are simulated retrospective examinations of future events, conducted as if those future events had already occurred. [Klein 2007] By combining the benefits of psychological safety with a shift in temporal perspective, premortems offer advantages for planners, because they can expose risks that might otherwise go unacknowledged. For more, see "Premortems," Point Lookout for March 23, 2022.
- Developing a statement of task goals
- A statement of task goals consists of two parts. First is a collection of descriptions of candidate goals, unranked as to priority or feasibility. Second, for each description, the statement includes the coordinates of the candidate goal in terms of the Eisenhower Matrix (Urgency by Importance), on a scale of 0 to 9 for each of the two coordinates. [Eisenhower 1954] If the group cannot agree on the description of one of the goals, the statement of task goals includes multiple competing descriptions. If the group cannot agree on the coordinates of one of the goals, multiple competing coordinate pairs are included. In this way, everyone feels heard and the disagreements are all made clear.
- Identifying indirectly obstructive behavior
- Indirectly obstructive behavior prevents the group from making progress toward Norming. Because these behaviors are indirect, they're deniable, which makes for difficulty addressing them. To identify a behavior is to describe it. To attribute a behavior is to name the person who exhibited that behavior. The former is helpful to anyone intent on helping the group come together and make progress toward Norming. The latter is helpful to anyone intent on blaming someone for the group's failure to come together and make progress toward Norming. Attribution is unnecessary if the description is clear. Attribution of obstructive behavior is itself obstructive and often toxic. For more, see "Covert Obstruction in Teams: II," Point Lookout for August 31, 2022.
Last words
The items above are merely possibilities for focusing sessions conducted during the Storming stage of a small group. They might work well for your group. But every organizational culture is unique. Another way to use these items is to regard them as examples of what you can do in your group if you were trying to plan sessions that would be more likely to uncover the kinds of frustrations and degrees of disagreement in your group that have caused problems for your group in past efforts. Whatever you uncover during Storming becomes less likely to trip you up during Performing. ![]() First issue in this series
First issue in this series ![]() Top
Top ![]() Next Issue
Next Issue
Occasionally we have the experience of belonging to a great team. Thrilling as it is, the experience is rare. In part, it's rare because we usually strive only for adequacy, not for greatness. We do this because we don't fully appreciate the returns on greatness. Not only does it feel good to be part of great team — it pays off. Check out my Great Teams Workshop to lead your team onto the path toward greatness. More info
More about Tuckman's sequence of small group development
 Reaching Agreements in Technological Contexts [December 7, 2022]
Reaching Agreements in Technological Contexts [December 7, 2022]- Reaching consensus in technological contexts presents special challenges. Problems can arise from interactions between the technological elements of the issue at hand, and the social dynamics of the group addressing that issue. Here are three examples.
 The Politics of Forming Joint Leadership Teams [January 4, 2023]
The Politics of Forming Joint Leadership Teams [January 4, 2023]- Some teams, business units, or enterprises are led not by individuals, but by joint leadership teams of two or more. They face special risks that arise from both the politics of the joint leadership team and the politics of the organization hosting it.
 Tuckman's Model and Joint Leadership Teams [January 18, 2023]
Tuckman's Model and Joint Leadership Teams [January 18, 2023]- Tuckman's model of the stages of group development, applied to Joint Leadership Teams, reveals characteristics of these teams that signal performance levels less than we hope for. Knowing what to avoid when we designate these teams is therefore useful.
 Beating the Layoffs: II [November 20, 2024]
Beating the Layoffs: II [November 20, 2024]- If you work in an organization likely to conduct layoffs soon, keep in mind that exiting voluntarily can carry advantages. Here are some advantages that relate to collegial relationships, future interviews, health, and severance packages.
 White Water Rafting as a Metaphor for Group Development [December 4, 2024]
White Water Rafting as a Metaphor for Group Development [December 4, 2024]- Tuckman's model of small group development, best known as "Forming-Storming-Norming-Performing," applies better to development of some groups than to others. We can use a metaphor to explore how the model applies to Storming in task-oriented work groups.
 Subgrouping and Conway's Law [December 18, 2024]
Subgrouping and Conway's Law [December 18, 2024]- When task-oriented work groups address complex tasks, they might form subgroups to address subtasks. The structure of the subgroups and the order in which they form depend on the structure of the group's task and the sequencing of the subtasks.
 The Storming Puzzle: I [December 25, 2024]
The Storming Puzzle: I [December 25, 2024]- Tuckman's model of small group development, best known as "Forming-Storming-Norming-Performing," applies to today's task-oriented work groups — if we adapt our understanding of it. If we don't adapt, the model appears to conflict with reality.
 The Storming Puzzle: II [January 1, 2025]
The Storming Puzzle: II [January 1, 2025]- For some task-oriented work groups, Tuckman's model of small group development doesn't seem to fit. Storming seems to be absent, or Storming never ends. To learn how this illusion forms, look closely at Satir's Change Model and at what we call a task-oriented work group.
 The Storming Puzzle: Six Principles [January 8, 2025]
The Storming Puzzle: Six Principles [January 8, 2025]- For some task-oriented work groups, Tuckman's model of small group development seems not to fit. Storming seems to be either absent or continuous. To learn how this illusion forms, look closely at the processes that can precipitate episodes of Storming in task-oriented work groups.
 The Storming Puzzle: Patterns and Antipatterns [January 15, 2025]
The Storming Puzzle: Patterns and Antipatterns [January 15, 2025]- Tuckman's model of small group development, best known as "Forming-Storming-Norming-Performing," applies to today's task-oriented work groups, if we understand the six principles that govern transitions from one stage to another. Here are some examples.
 Storming: Obstacle or Pathway? [January 22, 2025]
Storming: Obstacle or Pathway? [January 22, 2025]- The Storming stage of Tuckman's model of small group development is widely misunderstood. Fighting the storms, denying they exist, or bypassing them doesn't work. Letting them blow themselves out in a somewhat-controlled manner is the path to Norming and Performing.
 On Shaking Things Up [February 5, 2025]
On Shaking Things Up [February 5, 2025]- Newcomers to work groups have three tasks: to meet and get to know incumbent group members; to gain their trust; and to learn about the group's task and how to contribute to accomplishing it. General skills are necessary, but specifics are most important.
 On Substituting for a Star [February 12, 2025]
On Substituting for a Star [February 12, 2025]- Newcomers to work groups have three tasks: to meet and get to know incumbent group members; to gain their trust; and to learn about the group's task and how to contribute to accomplishing it. All can be difficult; all are made even more difficult when the newcomer is substituting for a star.
Footnotes
Your comments are welcome
Would you like to see your comments posted here? rbrenaXXxGCwVgbgLZDuRner@ChacDjdMAATPdDNJnrSwoCanyon.comSend me your comments by email, or by Web form.About Point Lookout
 Thank you for reading this article. I hope you enjoyed it and
found it useful, and that you'll consider recommending it to a friend.
Thank you for reading this article. I hope you enjoyed it and
found it useful, and that you'll consider recommending it to a friend.
This article in its entirety was written by a human being. No machine intelligence was involved in any way.
Point Lookout is a free weekly email newsletter. Browse the archive of past issues. Subscribe for free.
Support Point Lookout by joining the Friends of Point Lookout, as an individual or as an organization.
Do you face a complex interpersonal situation? Send it in, anonymously if you like, and I'll give you my two cents.
Related articles
More articles on Conflict Management:
 Totally at Home
Totally at Home- Getting home from work is far more than a question of transportation. What can we do to come home totally
— to move not only our bodies, but our minds and our spirits from work to home?
 Toxic Conflict in Virtual Teams: Virtuality
Toxic Conflict in Virtual Teams: Virtuality- In virtual teams, toxic conflict sometimes seems to erupt spontaneously. People who function effectively
in co-located teams can find themselves repeatedly embroiled in conflicts that seem to lack specific
causes. What triggers toxic conflict in virtual teams?
 Patterns of Conflict Escalation: II
Patterns of Conflict Escalation: II- When simple workplace disagreements evolve into workplace warfare, they often do so following recognizable
patterns. If we can recognize the patterns early, we can intervene to prevent serious damage to relationships.
Here's Part II of a catalog of some of those patterns.
 I Could Be Wrong About That
I Could Be Wrong About That- Before we make joint decisions at work, we usually debate the options. We come together to share views,
and then a debate ensues. Some of these debates turn out well, but too many do not. Allowing for the
fact that "I could be wrong" improves outcomes.
 Toxic Disrupters: Tactics
Toxic Disrupters: Tactics- Some people tend to disrupt meetings. Their motives vary, but they use techniques drawn from a limited
collection. Examples: they violate norms, demand attention, mess with the agenda, and sow distrust.
Response begins with recognizing their tactics.
See also Conflict Management for more related articles.
Forthcoming issues of Point Lookout
 Coming October 1: On the Risks of Obscuring Ignorance
Coming October 1: On the Risks of Obscuring Ignorance- A common dilemma in knowledge-based organizations: ask for an explanation, or "fake it" until you can somehow figure it out. The choice between admitting your own ignorance or obscuring it can be a difficult one. It has consequences for both the choice-maker and the organization. Available here and by RSS on October 1.
 And on October 8: Responding to Workplace Bullying
And on October 8: Responding to Workplace Bullying- Effective responses to bullying sometimes include "pushback tactics" that can deter perpetrators from further bullying. Because perpetrators use some of these same tactics, some people have difficulty employing them. But the need is real. Pushing back works. Available here and by RSS on October 8.
Coaching services
I offer email and telephone coaching at both corporate and individual rates. Contact Rick for details at rbrenaXXxGCwVgbgLZDuRner@ChacDjdMAATPdDNJnrSwoCanyon.com or (650) 787-6475, or toll-free in the continental US at (866) 378-5470.
Get the ebook!
Past issues of Point Lookout are available in six ebooks:
- Get 2001-2 in Geese Don't Land on Twigs (PDF, )
- Get 2003-4 in Why Dogs Wag (PDF, )
- Get 2005-6 in Loopy Things We Do (PDF, )
- Get 2007-8 in Things We Believe That Maybe Aren't So True (PDF, )
- Get 2009-10 in The Questions Not Asked (PDF, )
- Get all of the first twelve years (2001-2012) in The Collected Issues of Point Lookout (PDF, )
Are you a writer, editor or publisher on deadline? Are you looking for an article that will get people talking and get compliments flying your way? You can have 500-1000 words in your inbox in one hour. License any article from this Web site. More info
Follow Rick
Recommend this issue to a friend
Send an email message to a friend
rbrenaXXxGCwVgbgLZDuRner@ChacDjdMAATPdDNJnrSwoCanyon.comSend a message to Rick
![]() A Tip A Day feed
A Tip A Day feed
![]() Point Lookout weekly feed
Point Lookout weekly feed
 My blog, Technical Debt for Policymakers, offers
resources, insights, and conversations of interest to policymakers who are concerned with managing
technical debt within their organizations. Get the millstone of technical debt off the neck of your
organization!
My blog, Technical Debt for Policymakers, offers
resources, insights, and conversations of interest to policymakers who are concerned with managing
technical debt within their organizations. Get the millstone of technical debt off the neck of your
organization!